LABORATORY STUDY OF GROUTING METHOD DEVELOPMENT FOR LOOSE SAND IMPROVEMENT AGAINST LIQUEFACTION
Research Team : Dr. Cindarto Lie, Prof. Paulus P. Rahardjo, Ph.D, Dr. Eng. Imam A. Sadisun, ST., MT
Year : 2018
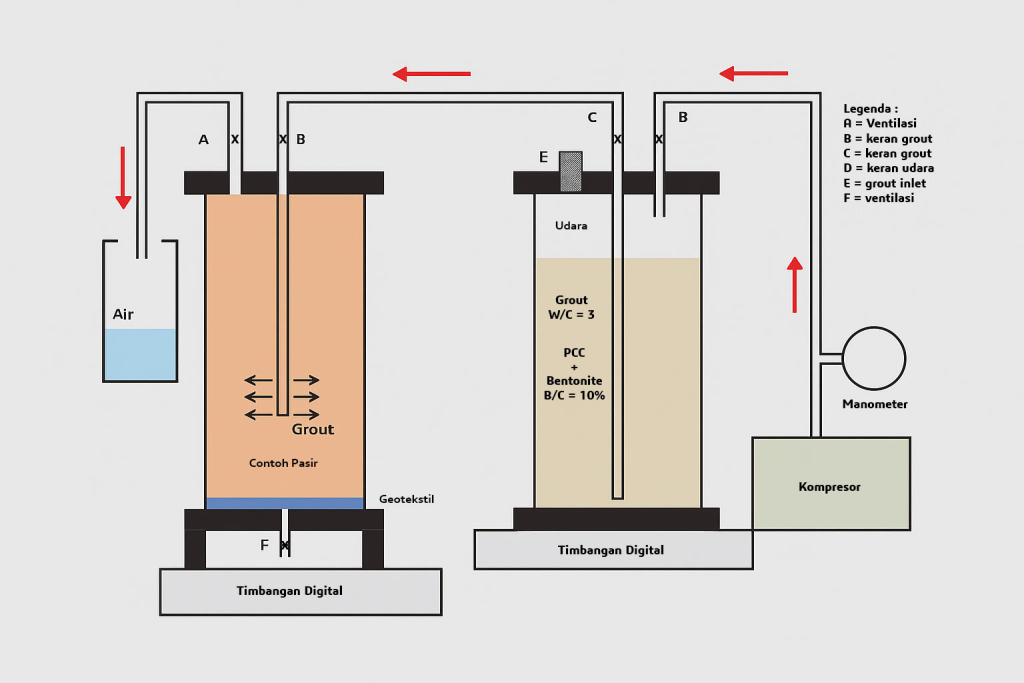
Abstract : Liquefaction is soil behaving like liquid during earthquake. Liquefaction only occurs on saturated loose fine sand soil which its grain 0.2 – 0.02 mm. Liquefaction can be devastating, causing failure and deformation to buildings, roads and bridges, flow liquefaction and landslide, wide spread settlement to lateral spreading of the ground. Thus research study in the laboratory has been carried out to study the application of grouting method for the improvement of loose fine sand soil. Grouting is a soil improvement method by injecting cementation liquid agent into the soil mass, after the grout solidified the soil consistency is improved. Fine sand sample from a reclamation project in North Jakarta has been used for this research and Portland Cement Composite, PCC which available in the local market was used as the base material for the grout.
Based on this research, grouting work effectively can reduce the liquefaction potential of loose fine sand by improving its density, shear strength, reducing state parameter value and finally increase the CRR, Cyclic Resistant Ratio of the treated soil.
The condition of liquefiable soil is saturated so that the grout injection directly induce pore water pressure build up and after dissipation causing consolidation of the liquefiable soil treated. The amount of grout content or the volume of grout per unit volume of soil mass treated directly proportional with the reduction of state parameter value and density improvement of the soil treated. It has been investigated as well the role of Bentonite in reducing bleeding and improving the stability of PCC cement grout. Finally this research is able to recommend formula and graphs that can be used to determine the amount of grout, it’s mixture and grout pressure for the improvement of liquefiable loose fine sand soil.